-
Bringing It All Together50 pts · 7775 Solves · 23 Solutions
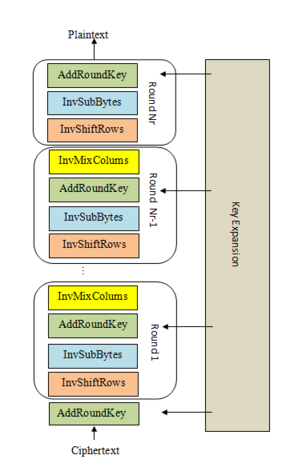
Apart from the KeyExpansion phase, we've sketched out all the components of AES. We've shown how SubBytes provides confusion and ShiftRows and MixColumns provide diffusion, and how these two properties work together to repeatedly circulate non-linear transformations over the state. Finally, AddRoundKey seeds the key into this substitution-permutation network, making the cipher a keyed permutation.
Decryption involves performing the steps described in the "Structure of AES" challenge in reverse, applying the inverse operations. Note that the KeyExpansion still needs to be run first, and the round keys will be used in reverse order. AddRoundKey and its inverse are identical as XOR has the self-inverse property.
We've provided the key expansion code, and ciphertext that's been properly encrypted by AES-128. Copy in all the building blocks you've coded so far, and complete thedecryptfunction that implements the steps shown in the diagram. The decrypted plaintext is the flag.
Yes, you can cheat on this challenge, but where's the fun in that?
The code used in these exercises has been taken from Bo Zhu's super simple Python AES implementation, so we've reproduced the license here.
Challenge files:
- aes_decrypt.py
- LICENSE
Resources:
- Rolling your own crypto: Everything you need to build AES from scratch
You must be logged in to submit your flag.
Level Up

You are now level Current level